Our Location
Elige tu idioma:
Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: What Seniors Need to Know About Each

When you're in your golden years, it's normal to feel like you must savor every moment more than ever. Whether you're out and about or cozying up for a movie night, participating in recreational activities is vital for your overall well-being. This is even more important if you have a chronic condition like diabetes.
It's essential to know what type of diabetes you have as management may differ. Type 1 diabetes classifies as an autoimmune disorder, while Type 2 arises from lifestyle factors. Both types of diabetes involve insulin production or usage, but they differ in several ways.
Here at Ocana Medical Center, we constantly educate our patients about the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes and provide individualized and compassionate care for diabetes in older adults. Be one of the many seniors living long and fulfilling lives with proper chronic disease management by giving us a call!
Diabetes Types Explained
It is well-known that diabetes in older adults is common. Whether you’re genetically predisposed or more at risk due to lifestyle factors, it’s completely normal to worry which type you have or may develop, if at all.
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. This occurs because the body either cannot produce or effectively utilize insulin, the hormone that helps transport glucose from the blood to the cells, allowing sugar to be used as energy.
Glucose that stays unused in your blood is dangerous and may damage your organs if untreated. In seniors, diabetes can lead to several complications, including an increased risk of heart disorders, kidney problems, vision issues, and slower healing of wounds.
What is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is a health disorder in which the body's immune system attacks and eliminates the insulin-producing beta cells from the pancreas. As a result, the body produces little or no insulin. This type of diabetes is more common in children and young adults, but it can occur at any age.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is an adverse metabolic condition that occurs when your body cannot make enough insulin or still produces insulin but cannot use it properly (insulin resistance). Unlike Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 often relates to lifestyle factors and tends to develop in adults over the age of 45, although it is becoming increasingly prevalent in younger people.
Risk Factors for Seniors
The risk factors for diabetes in seniors are characteristics or conditions that increase the likelihood of developing the disease. These factors can be biological, lifestyle-related, environmental, or genetic, and many are interconnected. For example, physical inactivity may lead to obesity, increasing insulin resistance. This interconnectedness amplifies the overall risk and prevalence of diabetes.
- Age-Related Factors
Aging is a notable risk factor for both types of diabetes. However, Type 2 diabetes is particularly prevalent among seniors. As we grow older, our bodies undergo inevitable changes that make us more susceptible to insulin resistance and impaired glucose tolerance.
- Genetics and Family History
A family history of diabetes increases the risk for both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. If you have close relatives with diabetes, you are more likely to develop the condition than those who have no diabetic family members or relatives. In this case, it would be wise to watch your blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Lifestyle and Diet
Unhealthy eating habits and a sedentary lifestyle typically contribute to the development of Type 2 diabetes. If your diet is usually high in sugars and processed foods and you rarely or never engage in physical activities, you have a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
- Weight and Obesity
Having excess weight is a significant risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. Seniors who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop insulin resistance, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Understand these risk factors to manage diabetes effectively. Combine them with lifestyle modifications and regular health check-ups to arrest or delay the onset of diabetes in older adults.
Symptoms of Diabetes in Elderly People
The symptoms of diabetes in seniors can often be subtle. They may overlap with signs of other age-related health issues, such as fatigue or blurred vision, making diagnosis challenging. Understanding the specific symptoms of diabetes in elderly individuals can help healthcare providers and seniors recognize the condition promptly and take appropriate action.
- Increased thirst and urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Extreme hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores or frequent infections
Specific Symptoms in Seniors
Seniors may experience additional symptoms like cognitive decline, increased infection susceptibility, and skin problems. If you experience most of these signs regularly, seek prompt medical advice.
Exploring Diabetes Diagnosis and Testing Options
Diagnosing diabetes involves several critical tests and assessments to determine blood sugar levels and overall health status. Routine examinations and early diagnosis are crucial for efficient management and prevention of complications associated with diabetes.
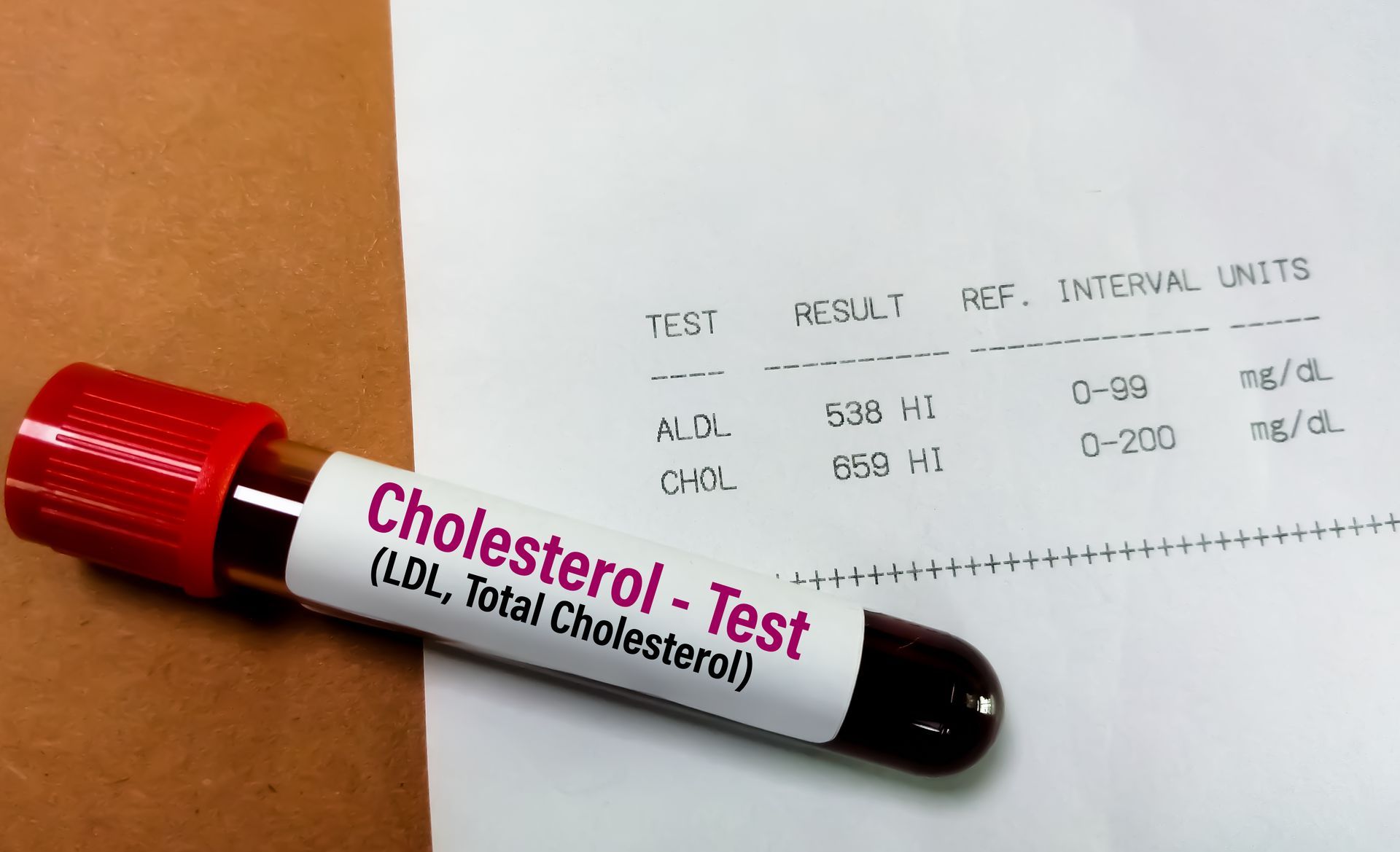
Blood Tests
The primary method for diagnosing diabetes involves blood tests, including:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test: Measures blood glucose after an overnight fast
- A1C Test: Measures your average blood glucose level over the past 2–3 months
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Checks how your body processes sugar before and after consuming a sugary substance
Regular Screenings for Seniors
Regular screenings are crucial for seniors, especially those with risk factors or symptoms of diabetes. This condition is easier to manage when detected early, reducing the risk of complications.
The high prevalence of diabetes in seniors, their elevated risk of complications, and the need for individualized care make early and accurate diagnosis through screening and testing essential for this population.
Managing Type 1 Diabetes in Older Adults
Older adults with Type 1 diabetes face unique challenges in managing their condition, including increased risk for severe hypoglycemia and other health complications. Treatment regimens should be modified to minimize these risks and improve quality of life. Here's a closer look at safe and efficient strategies:

Insulin Therapy
Seniors with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin daily. Many types of insulin are available, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting. The specific regimen will depend on your individual needs and medical advice.
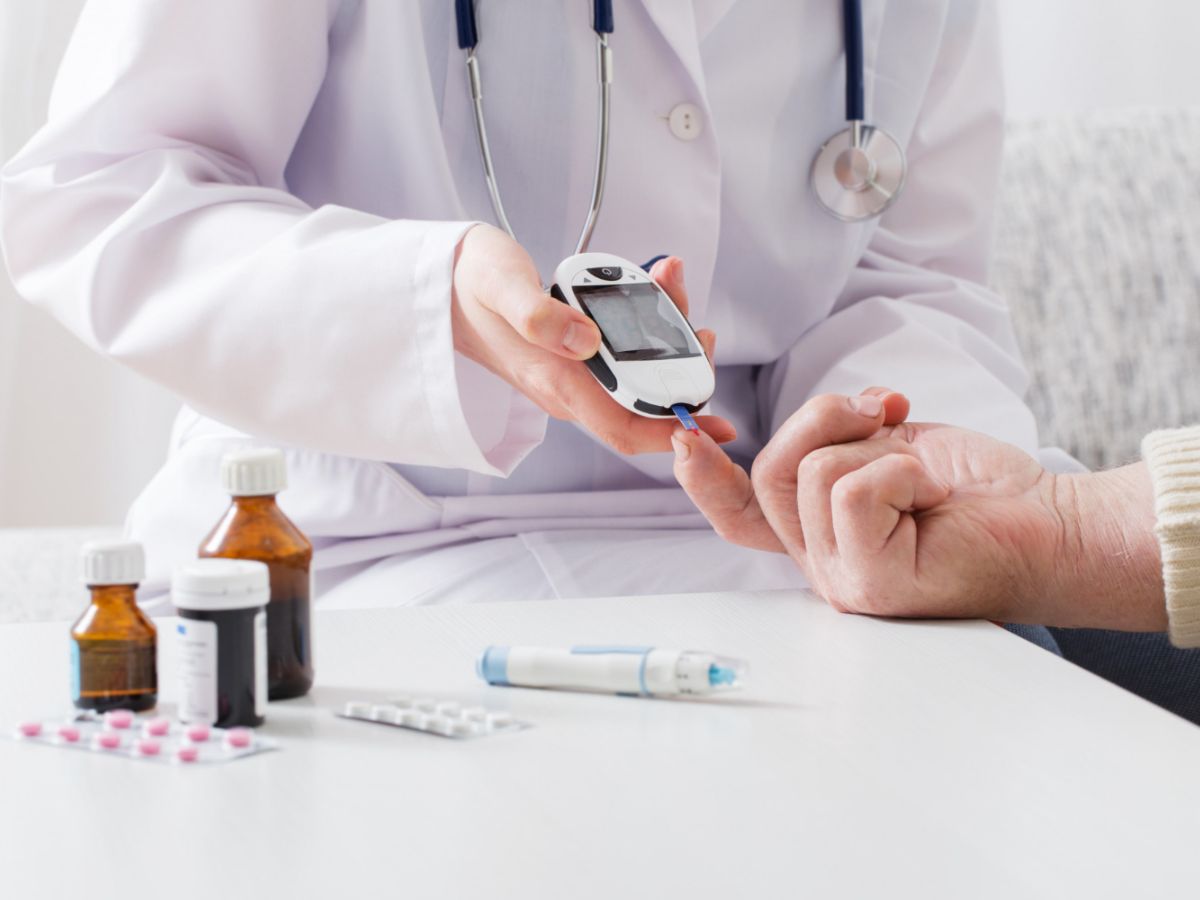
Monitoring Blood Sugar
Frequent blood sugar monitoring is essential for managing type 1 diabetes. You can use a glucometer to check your levels multiple times daily and adjust insulin doses accordingly. For seniors, the ideal blood sugar level is 80–180 mg/dL.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Maintaining healthy eating habits, being physically active, and engaging in stress management activities like yoga are crucial for seniors with type 1 diabetes. These lifestyle changes can help stabilize blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes in Older Adults
It is essential to take a multifaceted approach when managing type 2 diabetes in seniors, as poor management can lead to complications such as cardiovascular diseases, kidney failure, and other complications. Here are some of the most effective strategies:
Medications
Several types of medications can help manage Type 2 diabetes. These include metformin, sulfonylureas, and DPP-4 inhibitors. When treatments and lifestyle changes are not enough to control your diabetes, you will need insulin therapy.
Diet and Nutrition
A healthy diet is a strong foundation for managing Type 2 diabetes. Eat plenty of fruits like apples or cherries, vegetables like cabbage or spinach, whole grains like oats or barley, and lean proteins like chicken or nuts while avoiding processed and sugary foods.
Physical Activity
Light physical activity helps reduce blood sugar levels and improves insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 30 minutes of light to moderate exercise daily or most days of the week. Recommended exercises for controlling diabetes include walking, running, cycling, yoga, swimming, and weight training.
Weight Management
Losing weight significantly improves blood sugar control in seniors with Type 2 diabetes. A 5–10% body weight loss helps increase insulin sensitivity, which allows glucose to enter cells more efficiently, reducing blood sugar levels.
Insulin Pumps
A convenient alternative to daily injections, insulin pumps deliver insulin continuously to the body through the skin. These wearable devices can provide more precise insulin delivery and flexibility in lifestyle choices.
Ensure Diabetes Prevention and Management
Many seniors wake up to the reality of living with diabetes every day, and lifelong management can sound like an arduous journey. However, there is another matter worth celebrating: many older adults live long and fulfilling lives with diligent management, effective medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. For some, the only factor needed to achieve this reality is a reputable medical services provider to stand with them every step of the way.
Ocana Medical Center specializes in providing geriatric medical care for older adults with type 1 or 2 diabetes and similar conditions. With years of experience under his belt, Dr. Antonio L. Ocana, MD, leads a team of seasoned experts to provide personalized and compassionate geriatric care, using only evidence-based methods to treat and manage diabetes with proven success. We want you to experience a healthier and happier lifestyle during your golden years.
Overcome Diabetes Today!
“Respect. Compassion. Quality. Integrity. These are the values on which Ocana Medical Center was built. Our aim isn’t just to treat you today. We hope to earn your trust and be your healthcare provider for life.”
©2023 Ocana Medical Group, Inc.
USEFUL LINKS
GET IN TOUCH
Call Us Today
Send us Email
Our Location
Ocana Medical Center | All Rights Reserved.